What’s New in Data Management (June 2023)
Enhanced update data workflow
The workflow to append data to or update data in a hosted feature layer, or overwrite the contents of a hosted feature layer, has been updated and expanded into a more intuitive display of options. Separate workflows have been combined into a single workflow that you access from the Overview tab of the layer’s item page by clicking Update Data
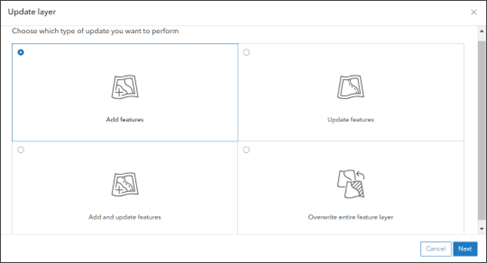

The option to append data is now referred to as adding features. Additional options for adding new data are also introduced, including specifying the time zone of source data being added and whether you want to update attributes only, or geometries and attributes.
Joined hosted feature layer views
A joined hosted feature layer view allows you to combine data from two different sublayers in a hosted feature or table layer based on a relationship between nonspatial attributes in each layer. You can join a layer to a layer, a layer to a table, or a table to a table.
Joined views are useful when you want to combine data from two layers and you need the data to dynamically update along with the source layers.
Created hosted feature layer views
If you need a different view of the data represented by a single hosted feature layer—for example, you want to apply different editor settings, styles, or filters—create a hosted feature layer view of that hosted feature layer. If you want to provide users with a single view that joins the data for two hosted feature layers, create a joined hosted feature layer view.
When you create a feature layer view, a new layer item is added to Content. This new layer is a view of the data in the source layers, which means edits made to the data in the source appear in the view. However, because the view is a separate item, you can change properties and settings on the view item separately from the hosted feature layer item from which it is created. For example, you can allow members of your organization to edit the hosted feature layer but share a read-only feature layer view with the public.
Only the owner of a hosted feature layer or an organization administrator can create a hosted feature layer view. This is different than copying a layer, which can be done by nonowners and even public users. Create a joined hosted feature layer view
A joined hosted feature layer view allows you to combine data from two different sublayers in a hosted feature or table layer based on a relationship between nonspatial attributes in each layer. You can join a layer to a layer, a layer to a table, or a table to a table.
Joined views are useful when you want to combine data from two layers and you need the data to dynamically update along with the source layers.
The following conditions must be met to create a joined hosted feature layer view:
- There must be a column in each source layer that you can use to define a SQL join between the two layers. You can define a one-to-one join or a one-to-many join.
Tip: Either determine what these columns are before you define the view, or you can preview the fields in each source layer while you’re defining the view.
- You must own both source hosted feature layers. Or, if you are an organization administrator, you can create a joined view from another user’s layers; however, both layers must be owned by the same user and the resulting view will be owned by that user.
One-to-one join options
You can use one of the following options to define a one-to-one join:
- Only keep the first matching record—The first record in the join layer that meets the join requirement will be included in the view. To control which record appears first, manipulate the sort field and order using the values in the Sort by and Sort order drop-down menus.
For example, to pull in the hospitals with the greatest number of beds in each city, sort by the bed_number field in the hospital layer and use a descending sort order.
- Summarize matching records—If there are multiple records in the join layer that match with one record in the target layer, you can define a calculation that performs a mathematical operation on a numeric or date field in the join layer, which will create a virtual field in the view that contains a single value for each matching record in the target.
For example, you could join a feature layer of cities with the hospital layer based on the state name, and calculate the minimum number of hospital beds in hospitals per city.
When you summarize matching records, the count of the summarized records is included as a column in the view layer by default.
Limitations of joined views
Keep in mind the following when using joined hosted feature layer views:
- Joined hosted feature layer views cannot be used to edit data.
- Joined hosted feature layer views cannot be used in offline maps.
- You cannot define filters, an area of interest, or restrict which fields are included in joined views.
- You cannot alter the join definition for a view. If you need to change which layers are in the view or change the join definition, delete the joined view and create a new one. Considerations when creating hosted feature layer views
Keep the following in mind when you create hosted feature layer views:
- You can overwrite the hosted feature layer from which the view was created to refresh the data only if the following are true:
- The parent hosted feature layer was published from a file in ArcGIS Online, not from ArcGIS Pro or ArcMap.
- The hosted feature layer view is not a joined feature layer view.
- You did not define an area of interest on the view.
- Usage is tracked separately for hosted feature layer views; however, feature storage is not charged for feature layer views. Storage is only charged for the primary hosted feature layer or layers from which the view was created
