Connecting the Built and Natural Environments with 3D GIS
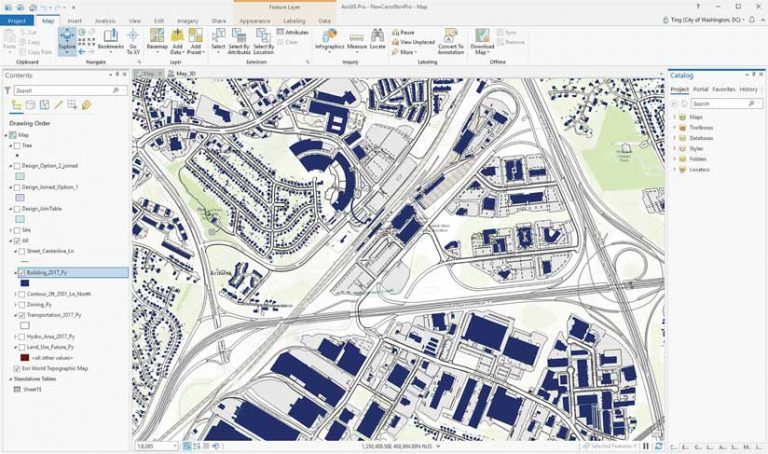
While GIS is commonly used in the urban planning and design process, it is normally used for site selection and analysis. Planners and designers use GIS to understand the topography, hydrology, demographics, and government regulations of an area, which informs the design of the project.
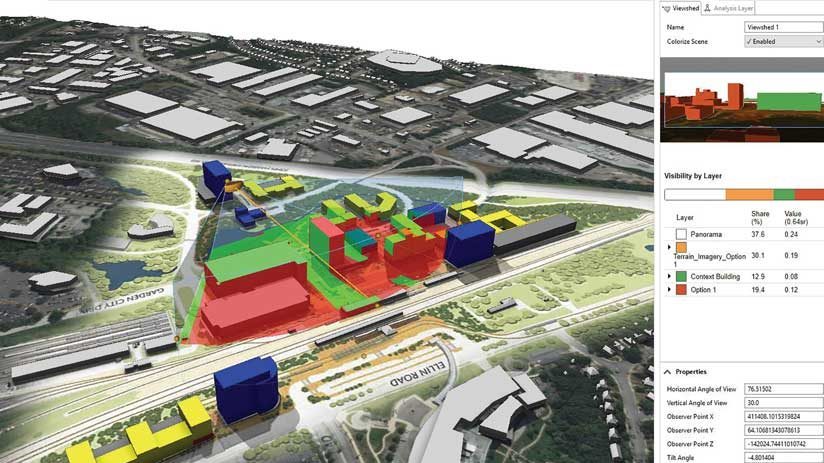
During the complex processes of urban planning and design, data collection, analysis, and visualization efforts are used to support decision-making, according to Le An, a senior urban planner and urban designer at Gensler’s Washington, DC, office. He notes that the rapid development of 3D and interactive GIS technology benefit urban planners, who can now adopt a more integrative and dynamic approach to managing and moderating planning and design tasks. This better serves the communities in which these projects are being built.
“We use both speculative site study and real-world urban design projects to develop and test our development framework. This enables us to integrate real-world GIS data, quickly create plans and models for multiple scenarios, evaluate the metrics, and perform spatial analytics of potential impacts,” said An. The team uses visualizations created in Esri CityEngine, web scenes, and ArcGIS StoryMaps to communicate ideas and designs to clients and stakeholders more effectively through the interactive 3D web applications.
The standard approach for most design firms is to show visualizations to clients as Microsoft PowerPoint presentations or as printed drawings. Sometimes 3D rendering companies are hired to create 3D models of proposed concepts. Unfortunately, all these methods provide only static representations.